Sale!
Description
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.

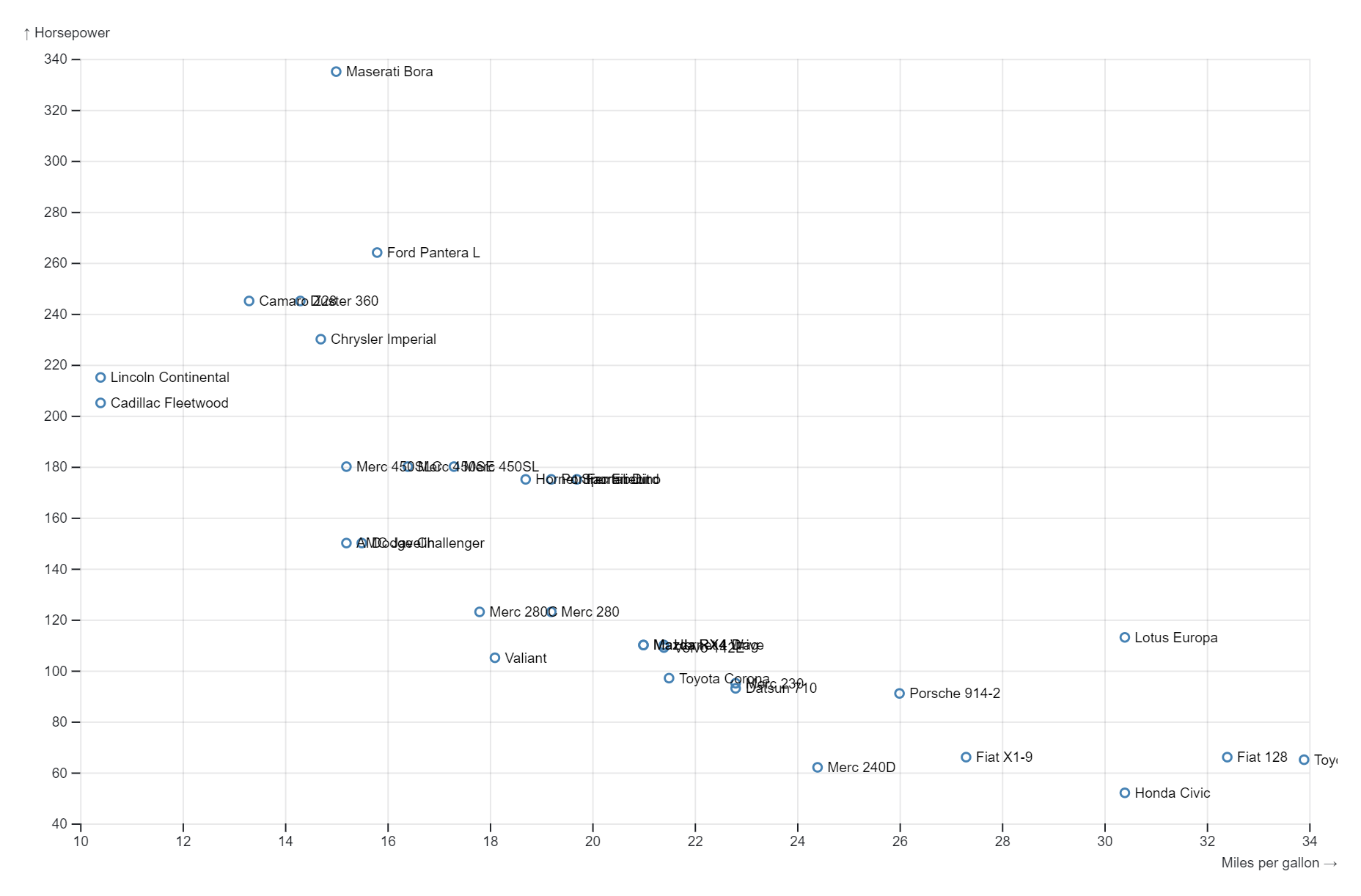
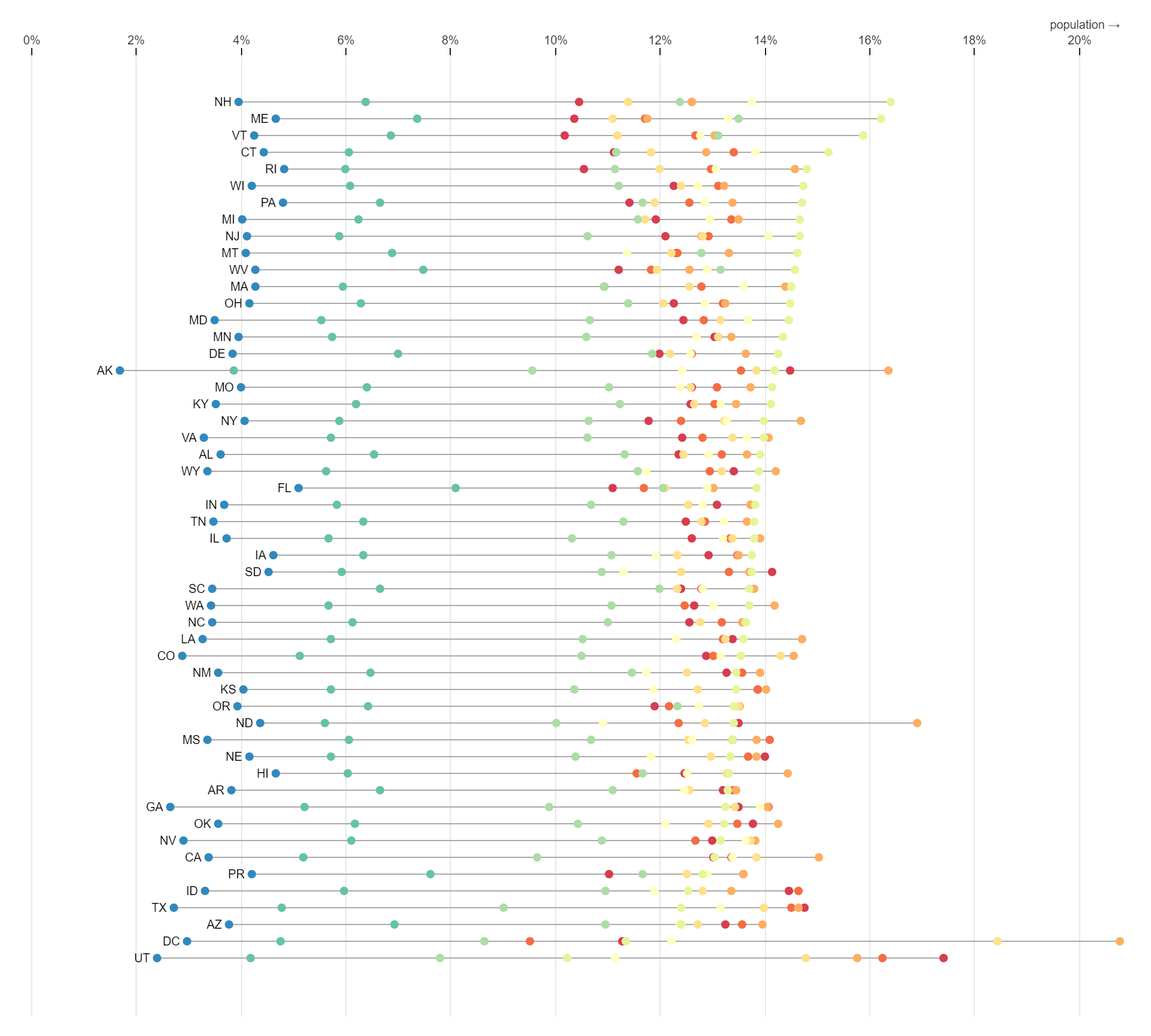
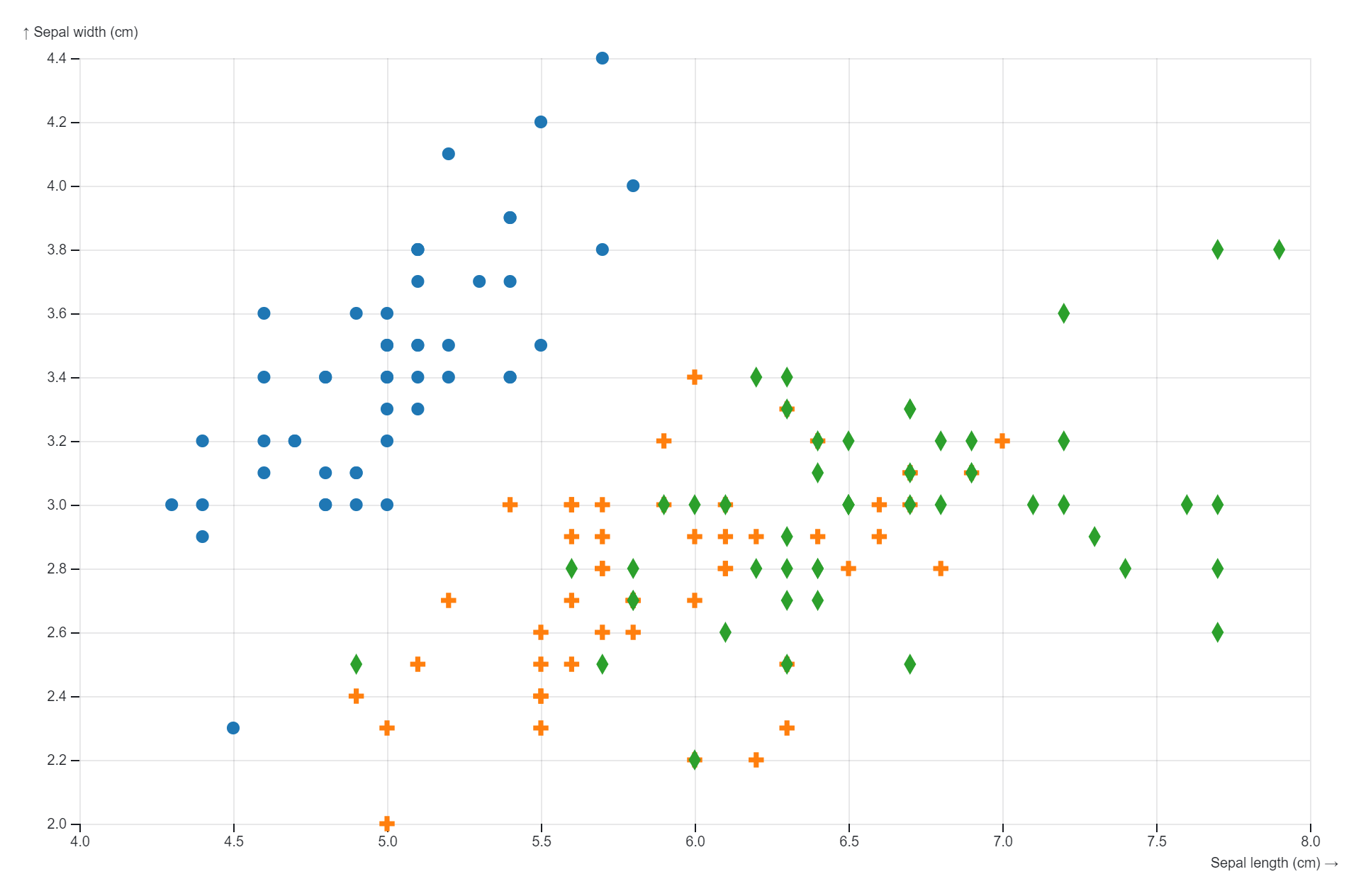

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.