Description
Description :
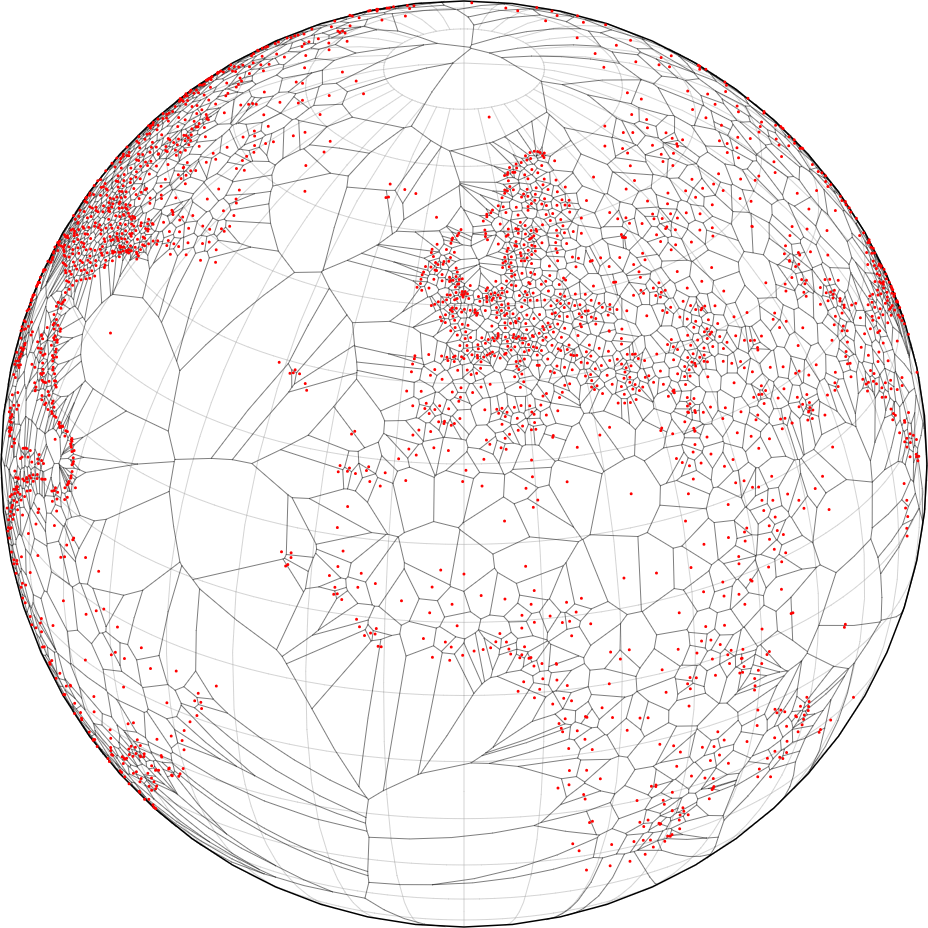
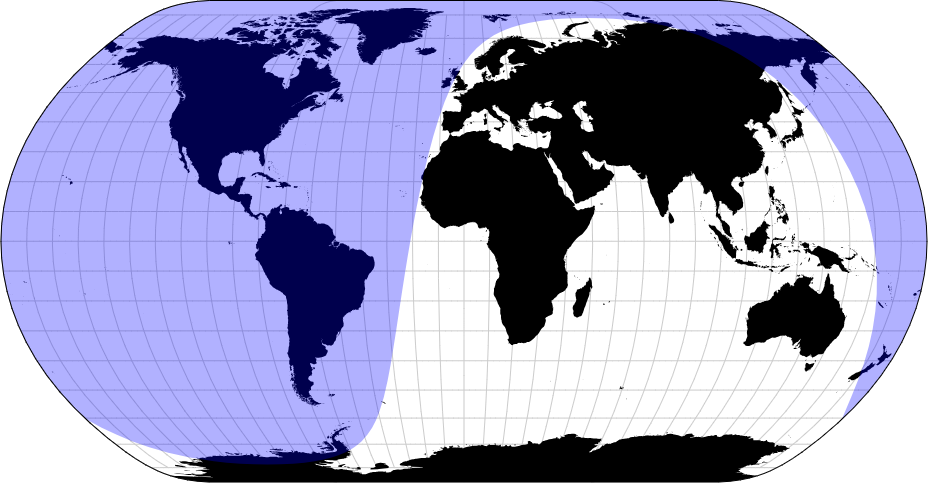
The solar terminator, also known as the “twilight zone” or “twilight boundary,” is the line that separates the illuminated half of the Earth from the dark half during the transition between day and night. It represents the boundary between daylight and darkness, where the Sun is either rising or setting. The terminator moves across the Earth’s surface as the planet rotates, causing day and night cycles. It’s a key concept in understanding global time zones and has implications for various fields such as astronomy, meteorology, and navigation.
The solar terminator, also known as the twilight zone or the line of sunset or sunrise, serves several important purposes
- Defining Day and Night: The primary purpose of the solar terminator is to delineate the boundary between daylight and darkness on Earth’s surface. It marks the transition from daytime to nighttime (sunset) and from nighttime to daytime (sunrise), providing a clear indication of when each period begins and ends.
- Navigation: The solar terminator plays a crucial role in celestial navigation, especially for sailors and pilots. It helps determine the direction of travel relative to the position of the sun, allowing navigators to establish their orientation and course accurately.
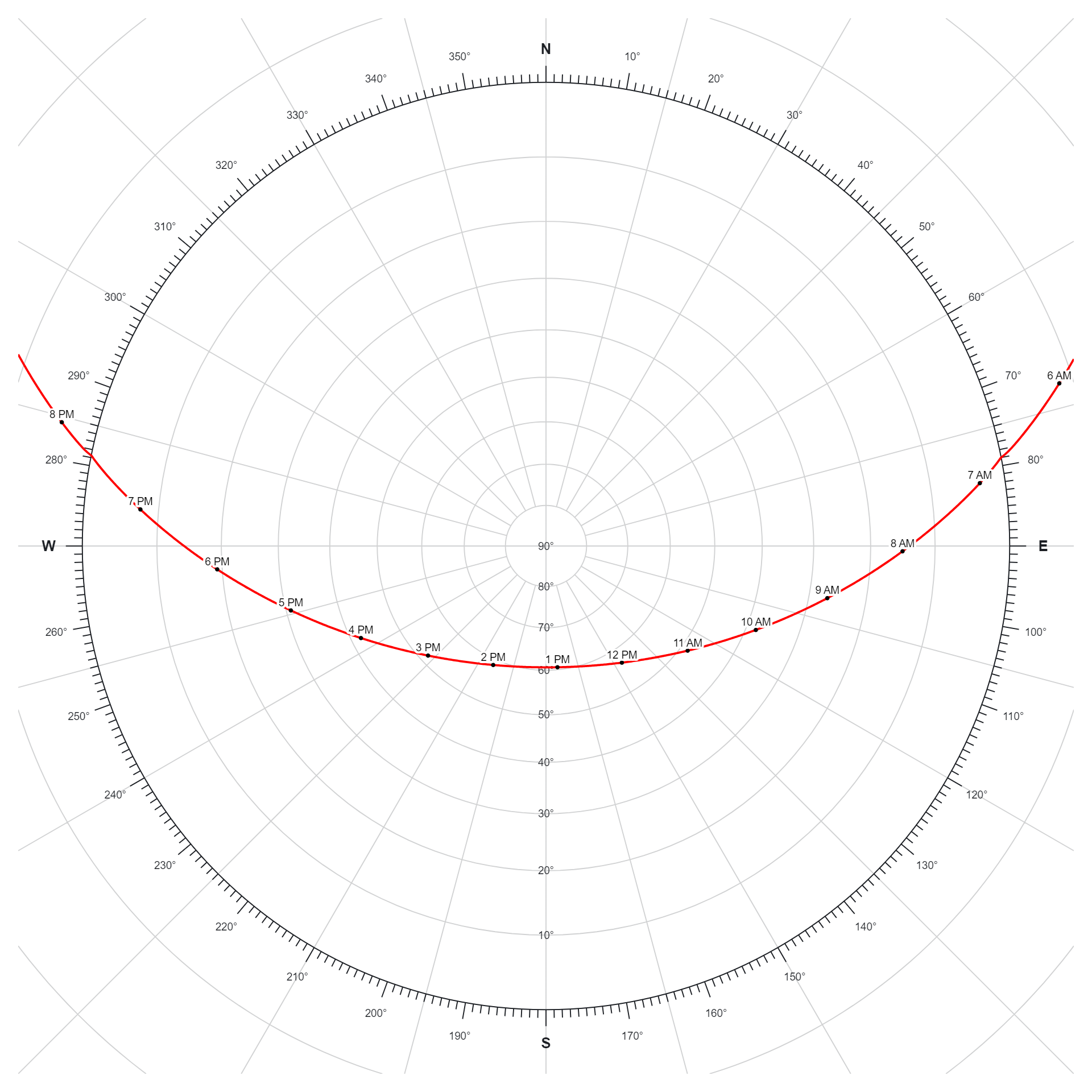
- Timekeeping: The position of the solar terminator is used to determine local solar time, which differs from standard time zones due to variations in the Earth’s rotation and orbit. Observing the movement of the solar terminator helps in tracking the progression of time throughout the day.
- Astronomy: Astronomers use the solar terminator to determine the best times for observing celestial objects. The transition between daylight and darkness minimizes the interference from sunlight, providing optimal conditions for stargazing and astronomical observations.
- Climate and Weather Studies: The solar terminator influences atmospheric phenomena such as temperature changes, cloud formation, and the onset of weather patterns. Studying the movement and characteristics of the solar terminator helps in understanding diurnal variations and seasonal changes in climate and weather.
- Ecology and Biology: The solar terminator affects the behavior and activities of various organisms, especially those that exhibit diurnal or crepuscular behavior. It regulates processes such as feeding, migration, and reproduction in animals, as well as photosynthesis and nutrient uptake in plants.
- Energy Production: The solar terminator is significant for renewable energy sources such as solar power. Solar panels operate most efficiently when they are perpendicular to incoming sunlight, making the position of the solar terminator important for optimizing energy production.
- Earth Observation: Satellite imagery and remote sensing technologies often rely on the solar terminator to capture images of the Earth’s surface under consistent lighting conditions. Observing changes in the solar terminator’s position over time helps monitor seasonal variations and environmental changes.
Overall, the solar terminator serves as a fundamental boundary that defines the rhythm of life on Earth, influencing various natural phenomena and human activities across different disciplines. Its precise determination and understanding are essential for a wide range of scientific, practical, and cultural purposes.
- Navigation: The solar terminator aids in navigation, especially for sailors, pilots, and travelers. It provides a reference point for determining directions, such as east or west, relative to the position of the sun, helping navigators establish their orientation and course accurately.
- Timekeeping: The position of the solar terminator is used to determine local solar time, which differs from standard time zones due to variations in the Earth’s rotation and orbit. Observing the movement of the solar terminator helps track the progression of time throughout the day.
- Astronomy: Astronomers use the solar terminator to determine the best times for observing celestial objects. The transition between daylight and darkness minimizes interference from sunlight, providing optimal conditions for stargazing and astronomical observations.
- Climate and Weather Studies: The solar terminator influences atmospheric phenomena such as temperature changes, cloud formation, and the onset of weather patterns. Studying the movement and characteristics of the solar terminator helps understand diurnal variations and seasonal changes in climate and weather.
- Ecology and Biology: The solar terminator affects the behavior and activities of various organisms, especially those that exhibit diurnal or crepuscular behavior. It regulates processes such as feeding, migration, and reproduction in animals, as well as photosynthesis and nutrient uptake in plants.
- Energy Production: The solar terminator is significant for renewable energy sources such as solar power. Solar panels operate most efficiently when they are perpendicular to incoming sunlight, making the position of the solar terminator important for optimizing energy production.
- Earth Observation: Satellite imagery and remote sensing technologies often rely on the solar terminator to capture images of the Earth’s surface under consistent lighting conditions. Observing changes in the solar terminator’s position over time helps monitor seasonal variations and environmental changes.
Overall, the solar terminator serves as a fundamental boundary that defines the rhythm of life on Earth, influencing various natural phenomena and human activities across different disciplines. Its precise determination and understanding are essential for a wide range of scientific, practical, and cultural purposes.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.
Related products
-
- Sale!
Hexbin Map
-
$ 15Original price was: $ 15.$ 10Current price is: $ 10. - Add to cart
-
- Sale!
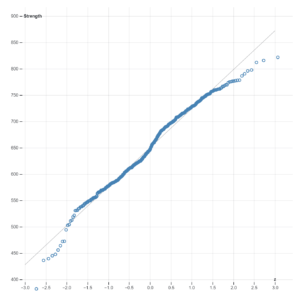
Normal Quantile Plot
-
$ 15Original price was: $ 15.$ 10Current price is: $ 10. - Add to cart
-
- Sale!
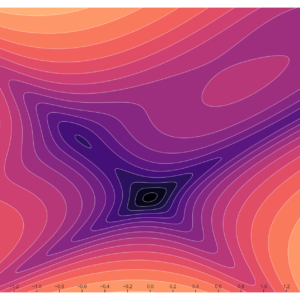
Contours
-
$ 15Original price was: $ 15.$ 10Current price is: $ 10. - Add to cart

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.