Sale!
Description
Extended Shepard’s interpolation is an extension of the Shepard’s method, which is a mathematical technique used for interpolating values within a set of data points. In Shepard’s interpolation, the value at a given point is estimated based on the weighted average of nearby data points, with weights determined by the distance between the point and the data points. Extended Shepard’s interpolation enhances this method by incorporating additional factors or considerations into the interpolation process, such as local trends, curvature, or boundary conditions, to improve the accuracy and reliability of the interpolated values.
Uses:
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Extended Shepard’s interpolation is used in GIS applications to interpolate elevation data, population density, or other geographic variables between known data points.
- Environmental Modeling: Environmental scientists use Extended Shepard’s interpolation to estimate pollution levels, air quality, or groundwater contamination at unsampled locations based on nearby monitoring data.
- Weather Forecasting: Meteorologists use Extended Shepard’s interpolation to interpolate weather data, such as temperature, humidity, or precipitation, between weather stations to create spatially continuous weather maps.
- Image Processing: Extended Shepard’s interpolation is used in image processing to interpolate missing or damaged pixels in digital images, enhancing image quality or restoring missing details.
- Medical Imaging: Medical researchers use Extended Shepard’s interpolation to interpolate medical imaging data, such as MRI or CT scans, to create smoother, higher-resolution images for diagnosis or analysis.
- Computer Graphics: Extended Shepard’s interpolation is used in computer graphics to interpolate color values, texture coordinates, or surface normals between vertices in 3D models, improving rendering quality and visual realism.
- Financial Modeling: Financial analysts use Extended Shepard’s interpolation to interpolate financial data, such as stock prices or interest rates, to fill in missing data points or create continuous time series for analysis or forecasting.
- Engineering Design: Engineers use Extended Shepard’s interpolation to interpolate physical properties, such as temperature distribution or stress levels, within mechanical or structural models to optimize design parameters.
- Remote Sensing: Remote sensing researchers use Extended Shepard’s interpolation to interpolate satellite or aerial imagery data, such as land cover classification or vegetation indices, to create spatially continuous maps for environmental monitoring or land management.
- Data Analysis and Visualization: Data analysts use Extended Shepard’s interpolation to fill in missing values or smooth noisy data in datasets, enabling more accurate analysis, visualization, and interpretation of the data.
Purposes:
- Data Smoothing: Extended Shepard’s interpolation smooths irregularities or noise in datasets by interpolating values between data points, creating a more continuous and visually appealing representation of the data.
- Data Completion: Extended Shepard’s interpolation fills in missing values or gaps in datasets by estimating values at unsampled locations based on nearby data points, enabling a more complete and comprehensive analysis of the data.
- Spatial Analysis: Extended Shepard’s interpolation enables spatial analysis by estimating values at arbitrary locations within a spatial domain, allowing researchers to explore spatial patterns, trends, and relationships in the data.
- Prediction and Forecasting: Extended Shepard’s interpolation predicts future values or trends by extrapolating from existing data points, providing insights into potential future outcomes or scenarios.
- Data Integration: Extended Shepard’s interpolation integrates disparate datasets by interpolating values between datasets, enabling cross-comparison and analysis of variables measured at different spatial or temporal resolutions.
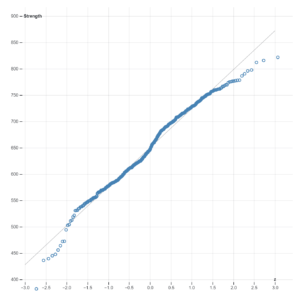
- Interpolation Accuracy: Extended Shepard’s interpolation improves the accuracy of interpolated values by incorporating additional factors or constraints into the interpolation process, such as local trends or boundary conditions.
- Spatial Visualization: Extended Shepard’s interpolation enhances spatial visualization by creating smooth, continuous surfaces or contours that accurately represent the underlying spatial patterns or variations in the data.
- Modeling and Simulation: Extended Shepard’s interpolation supports modeling and simulation by providing interpolated values for input parameters or variables within mathematical or computational models, improving model accuracy and reliability.
- Decision Support: Extended Shepard’s interpolation provides valuable information for decision-making by estimating values at specific locations or time points, guiding resource allocation, planning, or policy-making processes.
- Research and Exploration: Extended Shepard’s interpolation facilitates research and exploration by enabling scientists, engineers, and analysts to explore and analyze spatial or temporal data in greater detail, uncovering insights and patterns that may not be immediately apparent from raw data alone.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.