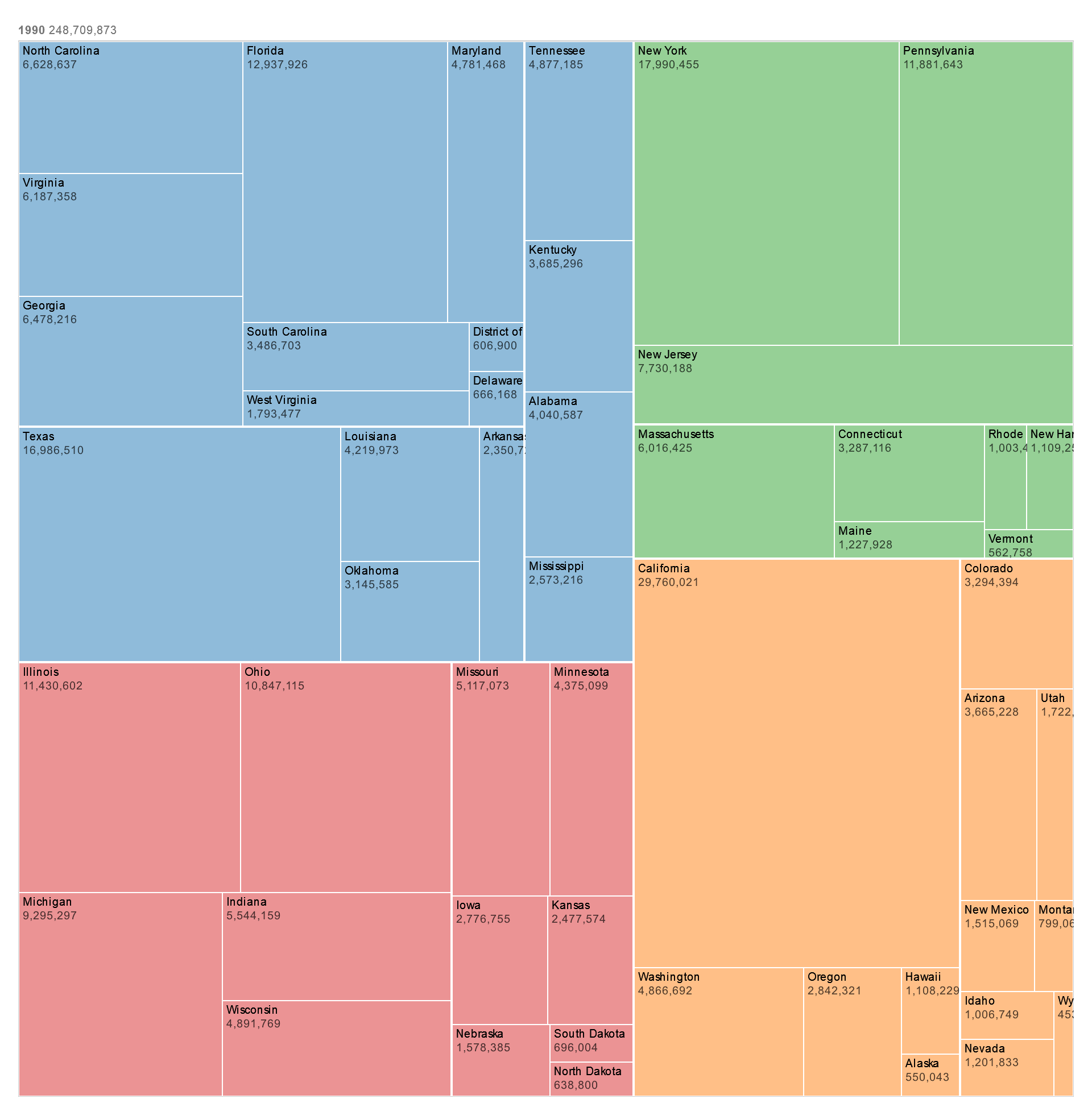
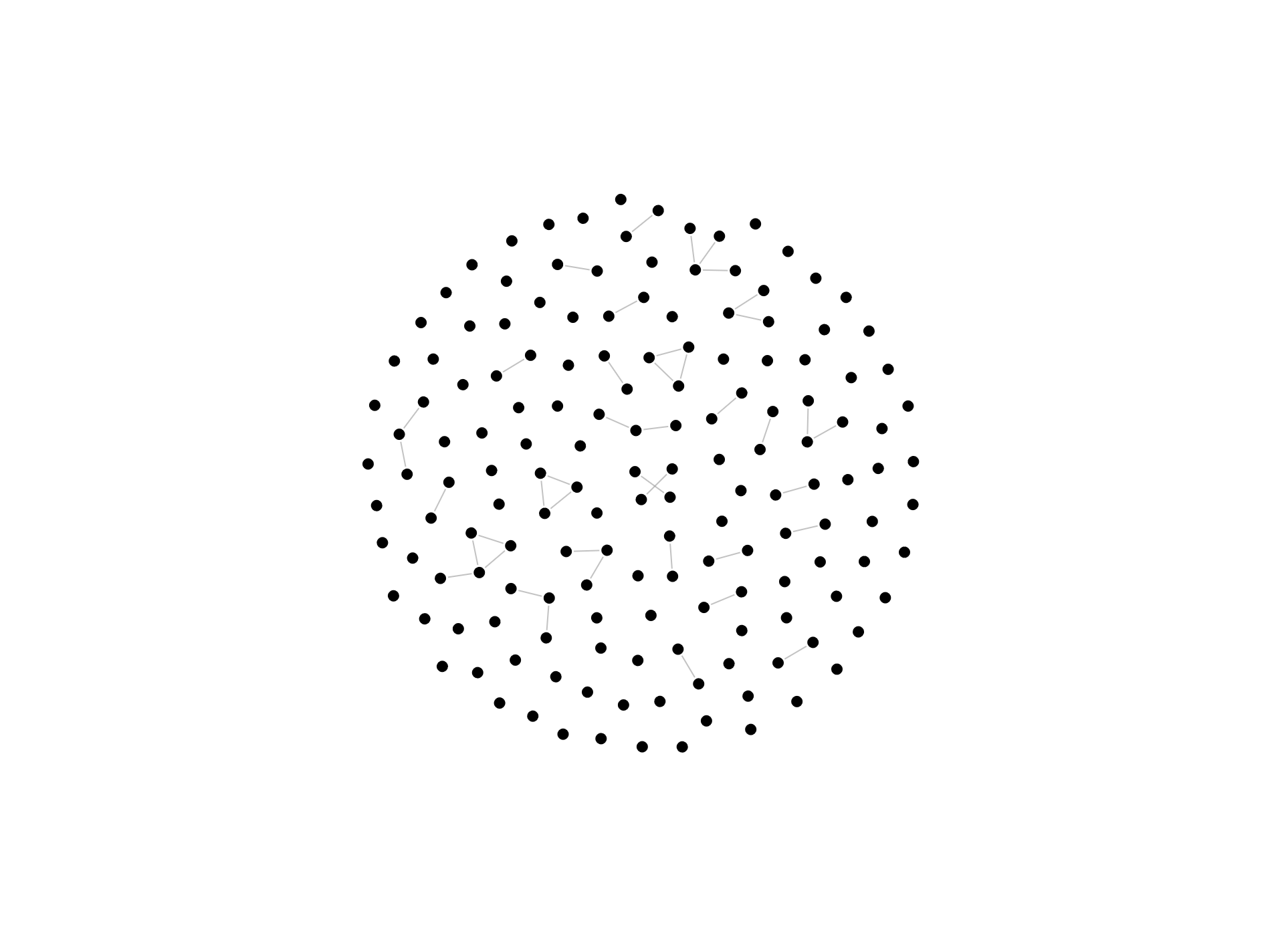
Description
A Temporal Force-Directed Graph Chart is a dynamic visualization tool that represents the evolution of a network over time using force-directed graph layouts. Unlike static graph layouts, which depict a single snapshot of a network, temporal force-directed graphs animate the movement of nodes and edges over time, revealing how the network structure changes and evolves. The layout is determined by simulating physical forces between nodes, which repel each other while connected nodes are drawn closer together. As the network evolves, the layout adapts dynamically to reflect changes in node positions and edge connections, providing insights into the network’s temporal dynamics and structural evolution.
Uses:
- Social Network Analysis: Tracking the evolution of social networks over time, including changes in connections, communities, and influential nodes.
- Historical Network Reconstruction: Visualizing historical networks, such as trade routes, transportation networks, or communication networks, to understand their evolution and impact over time.
- Dynamic Collaboration Networks: Analyzing collaborative networks, such as co-authorship networks or professional affiliations, to study collaboration patterns and trends over time.
- Epidemiological Modeling: Simulating the spread of infectious diseases or contagions through dynamic network models to predict outbreaks and assess intervention strategies.
- Financial Transaction Analysis: Monitoring financial networks, such as banking transactions or stock market interactions, to detect anomalies, trends, and patterns over time.
- Dynamic Supply Chain Management: Managing supply chain networks by visualizing the flow of goods, materials, and information through dynamic network representations.
- Internet Traffic Analysis: Analyzing internet traffic patterns, such as website visits, communication flows, and data transfers, to optimize network performance and security measures.
- Temporal Citation Networks: Studying the evolution of citation networks in scholarly literature to track the dissemination of scientific knowledge and identify influential publications.
- Dynamic Infrastructure Monitoring: Monitoring critical infrastructure networks, such as power grids, transportation systems, or telecommunications networks, to identify vulnerabilities and optimize performance.
- Real-time Event Detection: Detecting and analyzing real-time events, such as natural disasters, social movements, or cyber attacks, by monitoring changes in dynamic network structures.
Purposes:
- Temporal Pattern Recognition: Facilitating the recognition of temporal patterns, trends, and anomalies within evolving network structures over time.
- Interactive Exploration: Supporting interactive exploration and analysis of dynamic networks by allowing users to interactively manipulate the visualization and control playback speed.
- Temporal Network Visualization: Providing a comprehensive visual representation of temporal network data, including node movements, edge dynamics, and structural changes.
- Data-driven Decision Making: Empowering decision-makers with actionable insights derived from the visualization of temporal network dynamics and evolution.
- Pattern Discovery: Facilitating the discovery of hidden patterns, correlations, and relationships within dynamic network datasets through visual analysis and exploration.
- Comparative Analysis: Supporting comparative analysis of different time periods, scenarios, or datasets by visualizing temporal changes in network structure and behavior.
- Forecasting and Prediction: Using temporal network visualizations to forecast future network trends, predict emergent phenomena, and anticipate potential changes in network behavior.
- Communication Aid: Serving as an effective communication tool for presenting complex temporal network data to stakeholders, clients, or colleagues in an accessible and understandable format.
- Behavioral Analysis: Understanding changes in network behavior, connectivity, and dynamics through the observation and analysis of temporal patterns and trends.
- Temporal Network Modeling: Using dynamic network visualizations to validate and refine temporal network models, algorithms, and simulation techniques through visual experimentation and analysis.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.