Sale!
Description
Description :
Purpose :
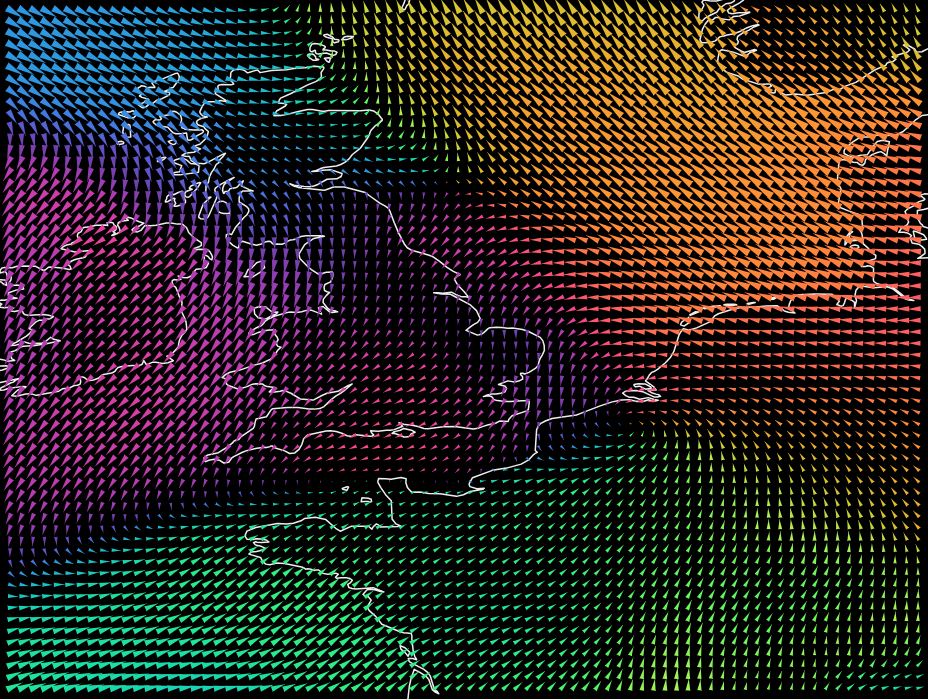
The purpose of GeoTIFF contours is to provide a digital representation of elevation data in the form of contour lines within a GeoTIFF raster image. Contour lines depict points of equal elevation on the Earth’s surface and are widely used in various fields for terrain visualization, analysis, and mapping. Here are some specific purposes of GeoTIFF contours:
- Terrain Visualization: GeoTIFF contours allow users to visualize the topography of an area by displaying contour lines that connect points of equal elevation. This visualization helps in understanding the shape, slope, and relief of the terrain, which is valuable for cartographic purposes, land management, and outdoor recreation.
- Elevation Analysis: GeoTIFF contours enable quantitative analysis of elevation data, such as calculating elevation profiles, slope gradients, and aspect angles. These analyses are used in hydrology, geology, environmental science, and engineering for studying terrain characteristics, assessing terrain suitability, and planning infrastructure projects.
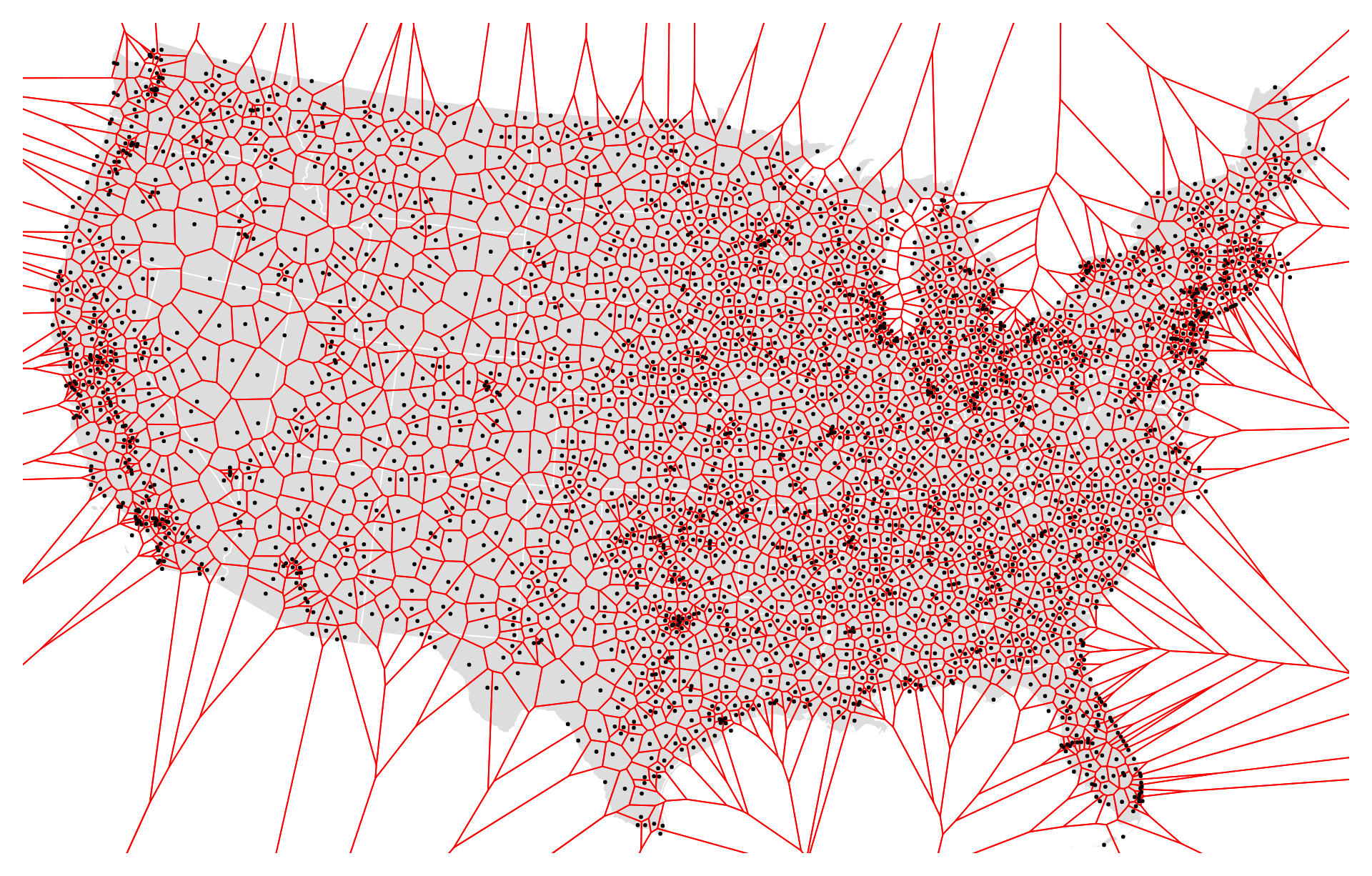
- Map Production: GeoTIFF contours are commonly used in map production to create topographic maps, trail maps, and land use maps. Contour lines provide essential geographic information that aids in map interpretation, navigation, and spatial analysis.
- 3D Visualization: GeoTIFF contours can be used to generate three-dimensional (3D) visualizations of terrain surfaces, allowing users to explore and interact with the landscape from different perspectives. 3D visualization enhances understanding of terrain features and facilitates communication of spatial information.
- Precision Agriculture: In agriculture, GeoTIFF contours are used for precision farming applications such as soil analysis, drainage planning, and crop management. Contour maps help farmers identify areas with specific elevation characteristics, optimize irrigation and drainage systems, and plan crop planting and harvesting activities.
- Natural Resource Management: GeoTIFF contours support natural resource management efforts by providing information on slope, elevation, and landform distribution. Resource managers use contour data for land use planning, habitat assessment, wildfire risk analysis, and watershed management.
- Disaster Management: In disaster management, GeoTIFF contours are used for assessing terrain vulnerability, identifying flood-prone areas, and planning emergency response strategies. Contour maps help emergency responders and planners anticipate the impact of natural hazards and mitigate risks to communities and infrastructure.
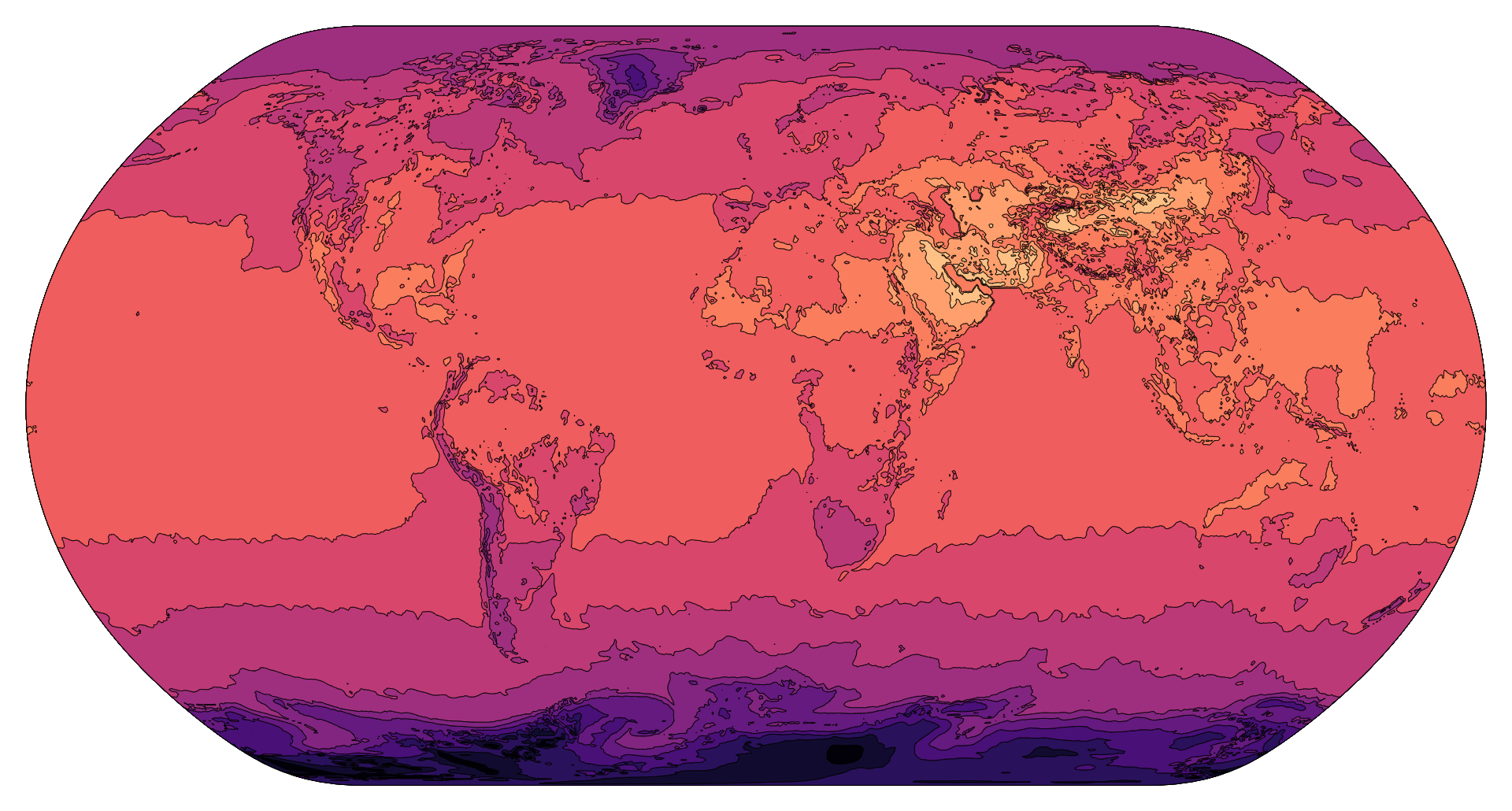
- Environmental Monitoring: GeoTIFF contours are used in environmental monitoring programs to track changes in terrain elevation over time. Monitoring elevation changes helps in assessing erosion rates, monitoring land subsidence, and studying the effects of climate change on landscape dynamics.
Uses :
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.