Description
Description :
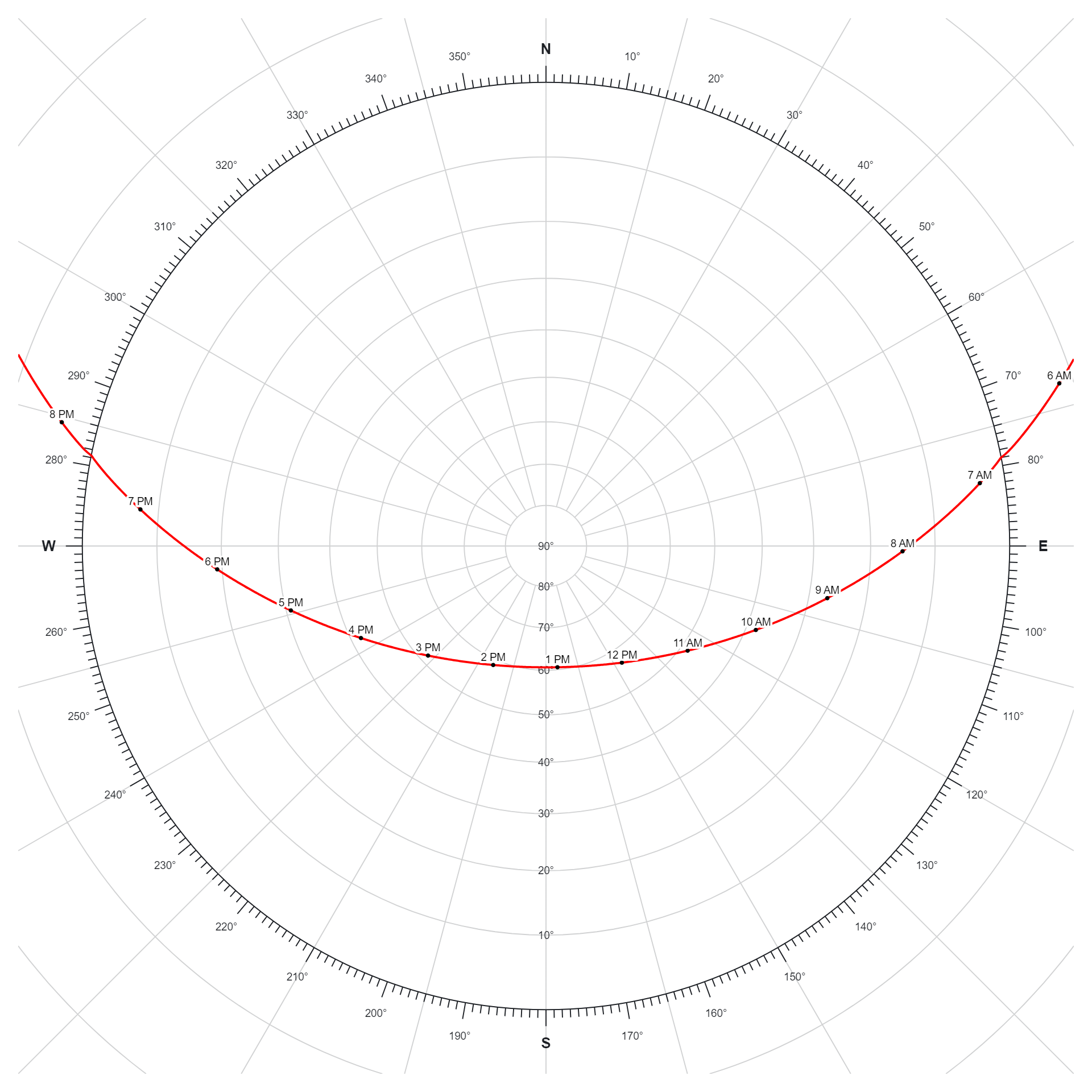
The solar path refers to the trajectory traced by the Sun across the sky during the course of a day. This path varies depending on factors such as latitude, time of year, and time of day. It rises in the east, reaches its highest point at solar noon, and sets in the west. The length and angle of the solar path influence the duration and intensity of sunlight received at a particular location, impacting phenomena like seasons, daylight hours, and solar energy potential. Understanding the solar path is essential for activities such as agriculture, architecture, and renewable energy planning.
Purpose :
The purpose of a solar path diagram is to visually represent the trajectory of the sun across the sky over the course of a day or year at a specific location. These diagrams are crucial tools for understanding the sun’s movement and its effects on various applications, including:
- Solar Energy Systems: Solar path diagrams help solar engineers and designers optimize the orientation and tilt angle of solar panels to maximize energy capture throughout the day and across different seasons. By analyzing the path of the sun, they can determine the most efficient placement of solar panels for optimal energy production.
- Building Design: Architects and engineers use solar path diagrams to design buildings that maximize natural light and minimize energy consumption. By understanding the sun’s path, they can strategically position windows, skylights, and shading devices to optimize daylighting and thermal comfort within buildings.
- Agriculture: Farmers and agricultural researchers use solar path diagrams to plan crop planting and optimize agricultural practices. By understanding the sun’s trajectory, they can determine optimal planting locations, spacing, and orientation of crops to maximize sunlight exposure and enhance crop yield.
- Urban Planning: Urban planners use solar path diagrams to design sustainable cities and communities that optimize natural light and energy efficiency. By considering the sun’s path, they can design streets, parks, and buildings to maximize sunlight exposure, promote outdoor comfort, and reduce reliance on artificial lighting and heating.
- Environmental Studies: Researchers studying climate, ecology, and environmental science use solar path diagrams to analyze the sun’s influence on temperature patterns, seasonal variations, and ecosystem dynamics. By understanding the sun’s trajectory, they can assess its effects on local climate, vegetation growth, and wildlife behavior.
- Outdoor Activities: Outdoor enthusiasts, hikers, and campers use solar path diagrams to plan outdoor activities and navigation. By understanding the sun’s movement, they can determine optimal times for hiking, camping, and outdoor recreation based on sunlight availability and direction.
Overall, the purpose of a solar path diagram is to provide valuable insights into the sun’s movement and its impact on various aspects of human life, from energy production and building design to agriculture, urban planning, environmental science, and outdoor activities. These diagrams serve as essential tools for optimizing our interactions with the sun and harnessing its energy more efficiently and sustainably.
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.