Sale!
Description
Description :
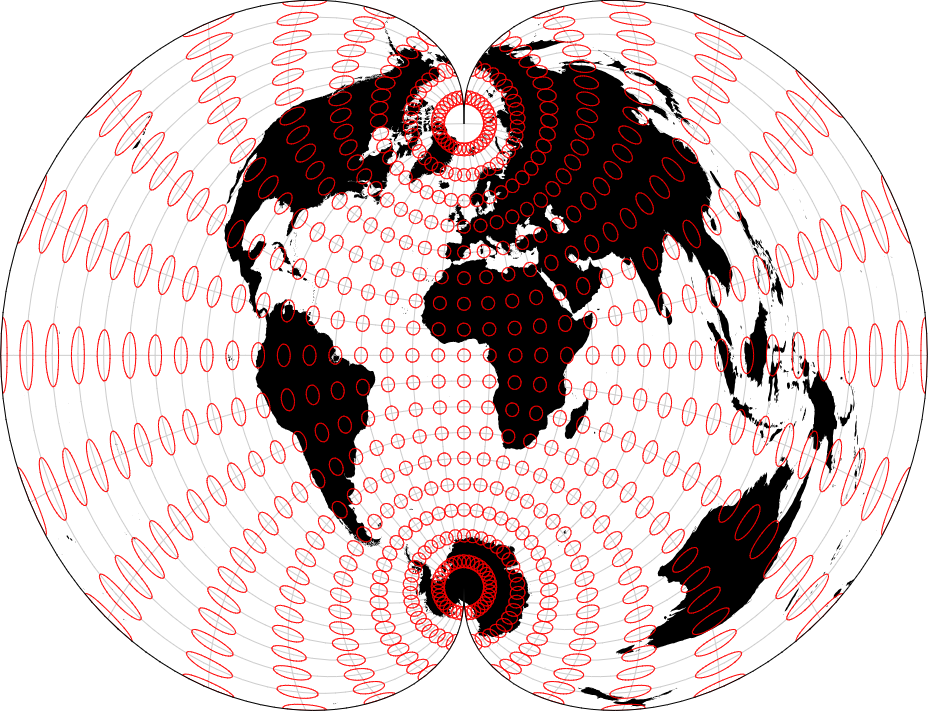
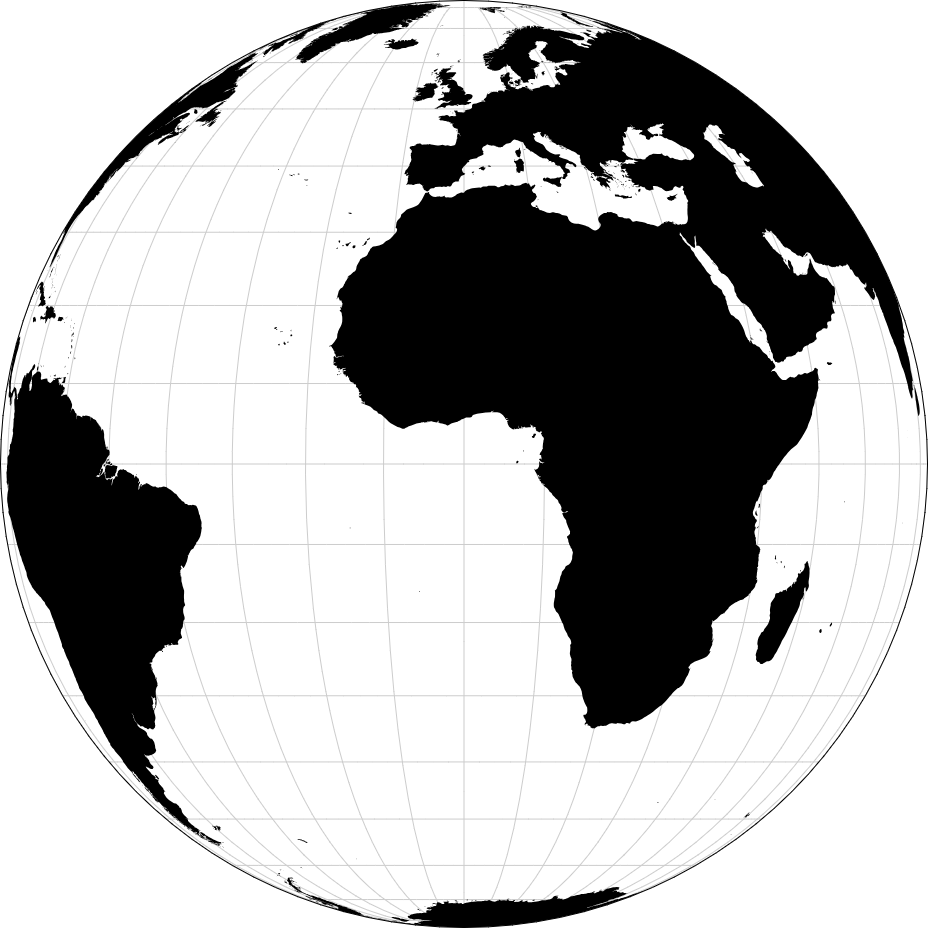
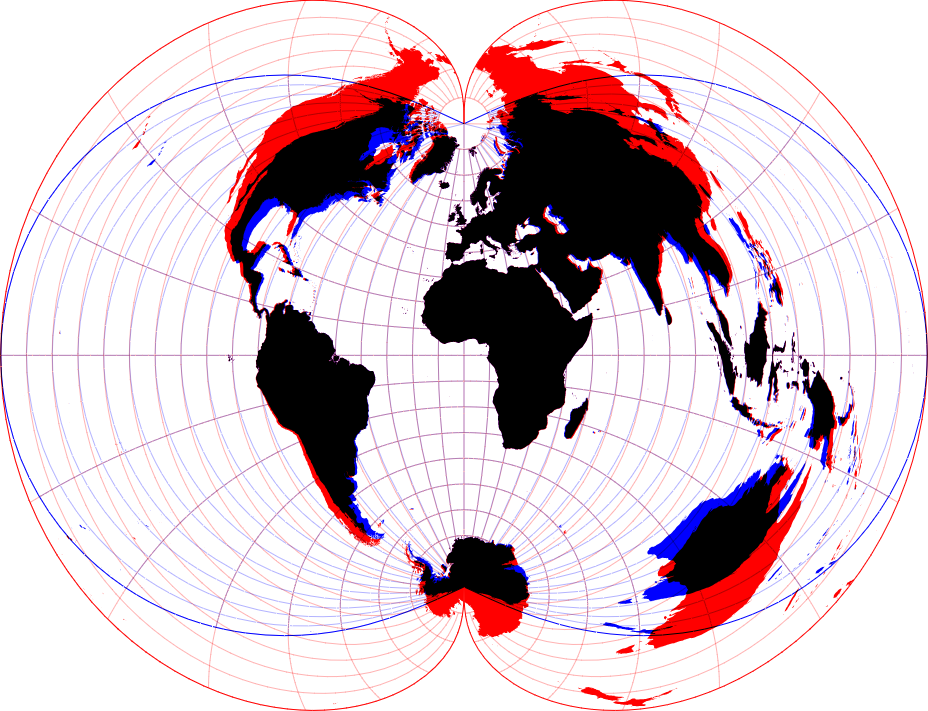
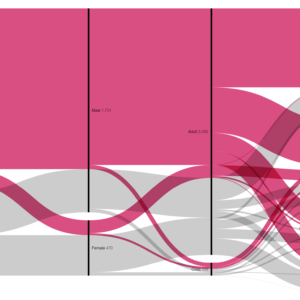
Projection comparison involves evaluating different map projections to understand how they distort the Earth’s surface on a flat map. Cartographers assess properties like shape, area, distance, and direction preservation in each projection to select the most suitable one for specific mapping tasks. By comparing projections side by side, users can identify distortions and trade-offs, ultimately making informed decisions about which projection best represents their geographic data. This process ensures accurate and effective map representation while minimizing distortion.
Purposes :
Uses :
Only logged in customers who have purchased this product may leave a review.


Reviews
There are no reviews yet.